Study Notes

Overview
Technology is a recurring and vital theme in the AQA GCSE Business specification. Examiners expect candidates to move beyond generic statements and demonstrate a clear understanding of how specific technologies impact the functional areas of a business: Marketing, Operations, and Human Resources. This involves analysing the trade-off between the high initial fixed costs of investment and the potential for long-term efficiency gains, such as lower unit costs and improved quality. A strong answer must always be grounded in the context of the business provided in the exam Item, showing a clear chain of reasoning (AO2 and AO3) that links a technological change to its ultimate impact on business objectives like profit, competitiveness, and growth. This guide will equip you with the specific terminology, analytical frameworks, and evaluation skills needed to confidently tackle any question on this topic.
Key Technological Applications
Marketing Technology
What it is: This area focuses on how businesses use technology to identify, anticipate, and satisfy customer needs more effectively. The two core technologies are E-commerce and M-commerce, supplemented by digital marketing techniques.
- E-commerce: The use of online platforms (websites) to sell products to a national or even global market, 24/7. This drastically reduces the need for expensive physical stores.
- M-commerce: A subset of e-commerce, focusing on transactions made through mobile devices like smartphones and tablets, often via dedicated apps.
- Digital Marketing: Includes social media campaigns, search engine optimisation (SEO), and targeted online advertising to reach specific customer demographics.
Why it matters: For the exam, you must link these technologies to marketing objectives. For example, e-commerce increases the potential market size (Place), while targeted social media adverts make promotional spending more efficient (Promotion).
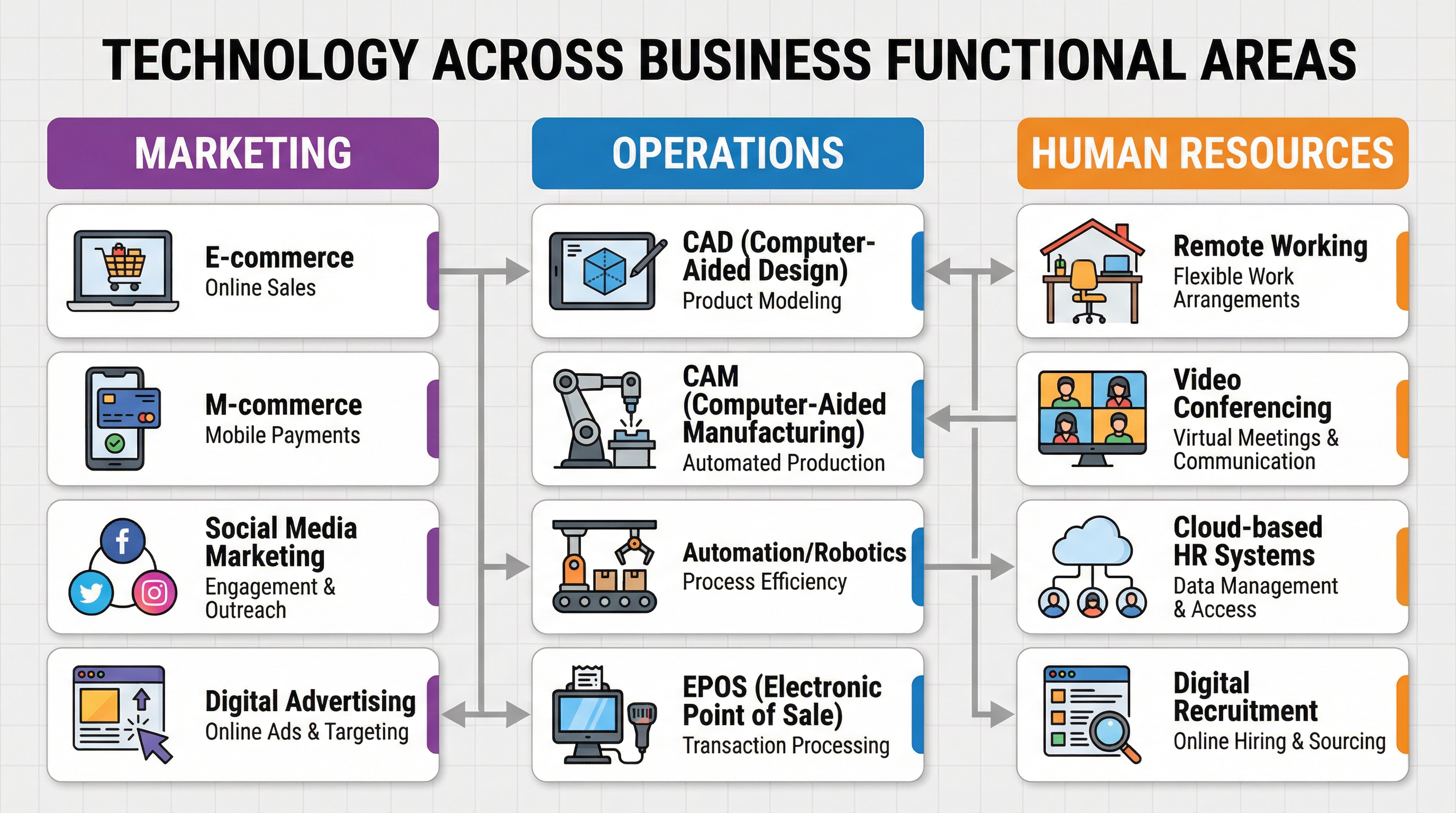
Operations Technology
What it is: This involves the use of machinery and computer systems to improve the production process. Key examples include CAD, CAM, and automation.
- CAD (Computer-Aided Design): Software used to create detailed 2D or 3D models of products before they are made. This allows for rapid prototyping and testing, reducing waste.
- CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): The use of computers to control the machinery that manufactures the product, such as robotic arms on a production line.
- Automation/Robotics: The wholesale replacement of human labour with machinery, leading to a highly capital-intensive production process. This results in high speed, precision, and consistency.
- EPOS (Electronic Point of Sale): Computerised tills that automatically update stock levels when a sale is made, providing real-time sales and stock data.
Why it matters: Credit is given for explaining how these technologies lead to greater efficiency. For example, CAM leads to lower variable costs per unit, improved quality consistency, and faster production times. EPOS improves cash flow by optimising stock levels.
Human Resources (HR) Technology
What it is: This concerns the use of technology to manage employees and working practices.
- Remote Working: The practice of employees working from home, enabled by cloud computing, collaboration software (e.g., Microsoft Teams), and video conferencing.
- Cloud-Based Systems: Software that allows for shared access to files and data from any location, facilitating flexible working.
Why it matters: Candidates should analyse the costs and benefits. Remote working can reduce a business's overhead costs (e.g., rent on office space) and potentially increase employee motivation. However, it can also create challenges in terms of communication, monitoring productivity, and maintaining a strong team culture.
Second-Order Concepts: The Core Trade-Off
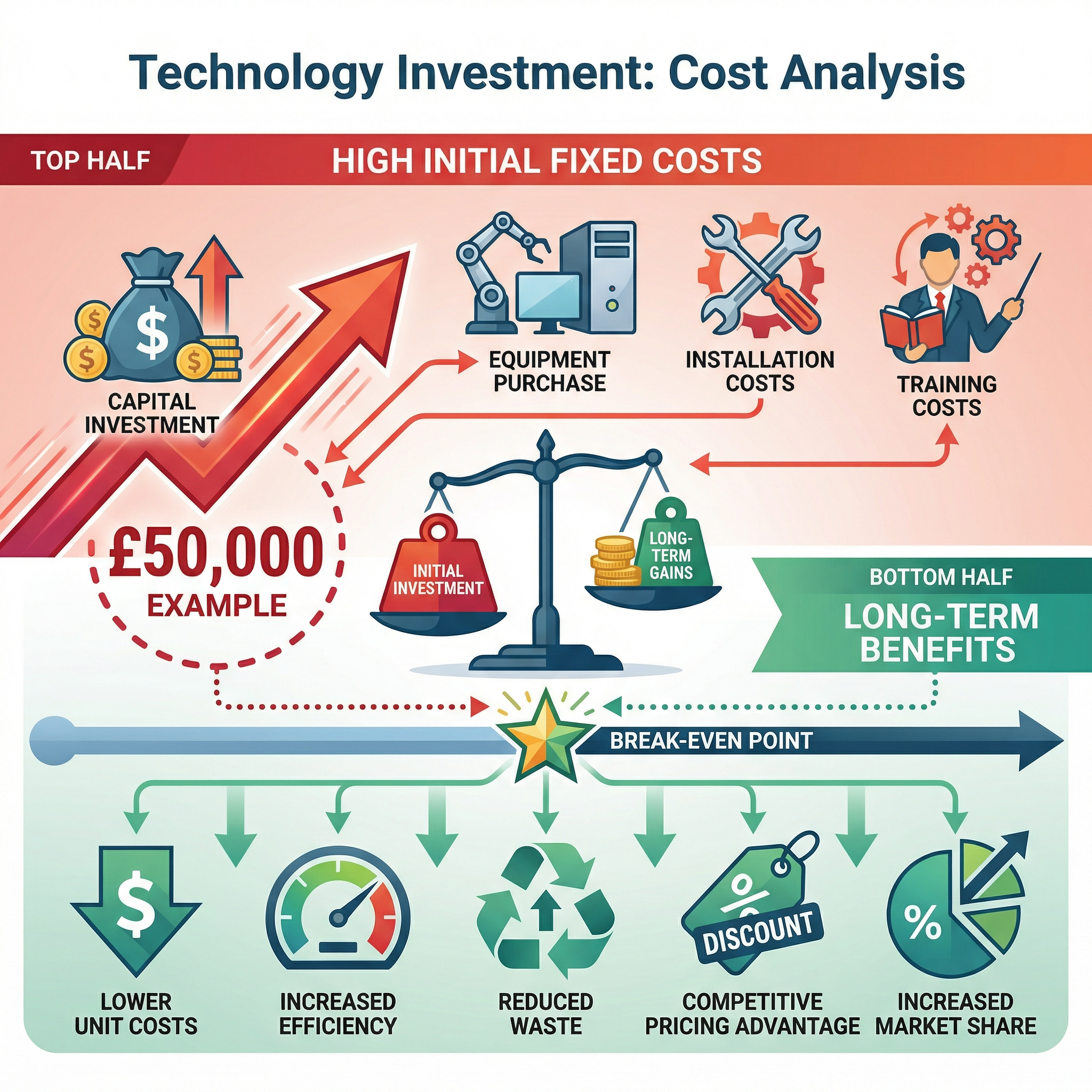
Cost vs. Benefit
At the heart of every technology question is a financial trade-off. Investing in technology almost always involves high initial fixed costs (e.g., buying the equipment, installation, training) but offers the promise of long-term benefits (e.g., lower variable costs, higher productivity, less waste). Evaluation questions (12 marks) require you to weigh these up in the context of the specific business. A small business with limited cash reserves will view this trade-off very differently from a large multinational corporation.
Impact on Stakeholders
Technology impacts various stakeholder groups:
- Owners/Shareholders: Benefit from increased profitability and long-term growth.
- Employees: May face redundancy due to automation, or benefit from flexible working arrangements. They may also require retraining.
- Customers: Often benefit from lower prices, better quality products, and the convenience of e-commerce.
