Study Notes

Overview
A business plan is a fundamental document for any new or existing business. For the WJEC GCSE Business exam, candidates are expected to demonstrate a thorough understanding of its components, its purpose for different stakeholders, and its role in monitoring business performance. Examiners are looking for more than just a list of what a business plan includes; they want to see that you can analyse its importance in different business contexts. This guide will walk you through the key areas you need to know, from securing that crucial bank loan to using the plan as a benchmark for success. We will explore how to structure your answers to gain maximum credit and avoid common pitfalls that cost candidates marks.
Key Components of a Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is essential. Examiners will award AO1 marks for correctly identifying the key sections. These sections are interconnected and provide a complete picture of the business.
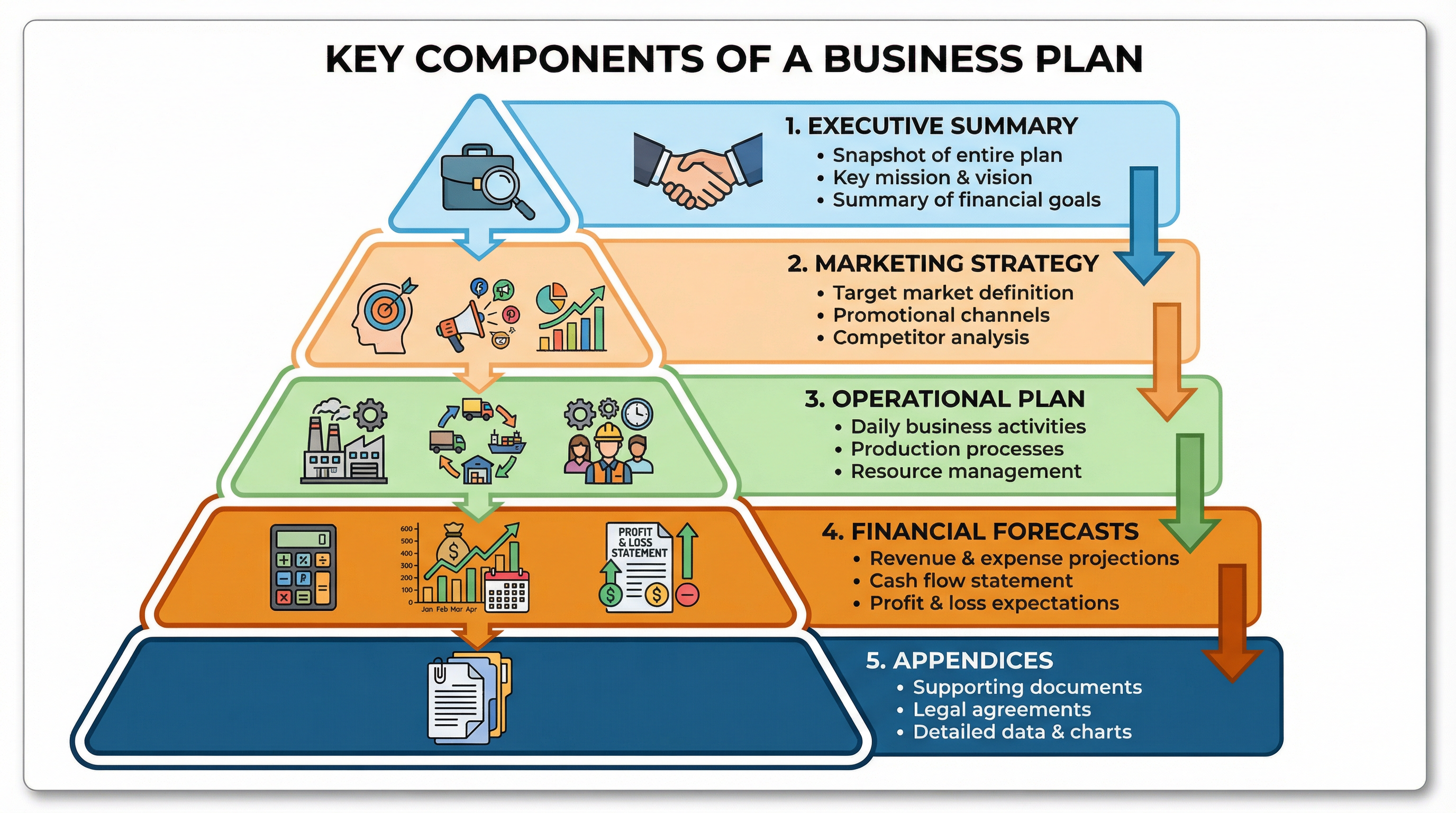
1. Executive Summary
This is a concise overview of the entire business plan. It should be written last, but it appears first in the document. Its purpose is to grab the reader's attention and provide a snapshot of the business concept, financial highlights, and key goals. For a bank manager or investor with limited time, this is the most important section.
2. Marketing Strategy
This section details how the business will attract and retain customers. It includes:
- Market Research: Analysis of the target market, industry trends, and competitors.
- Marketing Mix (4 Ps): Product, Price, Place, and Promotion strategies.
- Sales Forecasts: Realistic projections of sales revenue.
3. Operational Plan
This describes the day-to-day running of the business. It covers:
- Production Process: How the product will be made or the service delivered.
- Premises and Equipment: The physical location and resources needed.
- Suppliers: Who will provide the raw materials or stock.
- Legal Requirements: Necessary licenses, permits, and compliance with regulations.
4. Financial Forecasts
This is the numerical part of the plan and is critical for securing finance. It includes:
- Cash Flow Forecast: Predicts the monthly inflows and outflows of cash.
- Profit and Loss Account: Forecasts the business's profitability over a period (usually the first year).
- Break-Even Analysis: Calculates the point at which the business's total costs equal its total revenue.
The Purpose of a Business Plan for Different Stakeholders
Different stakeholders use a business plan for different reasons. Understanding this is key to achieving AO2 and AO3 marks.
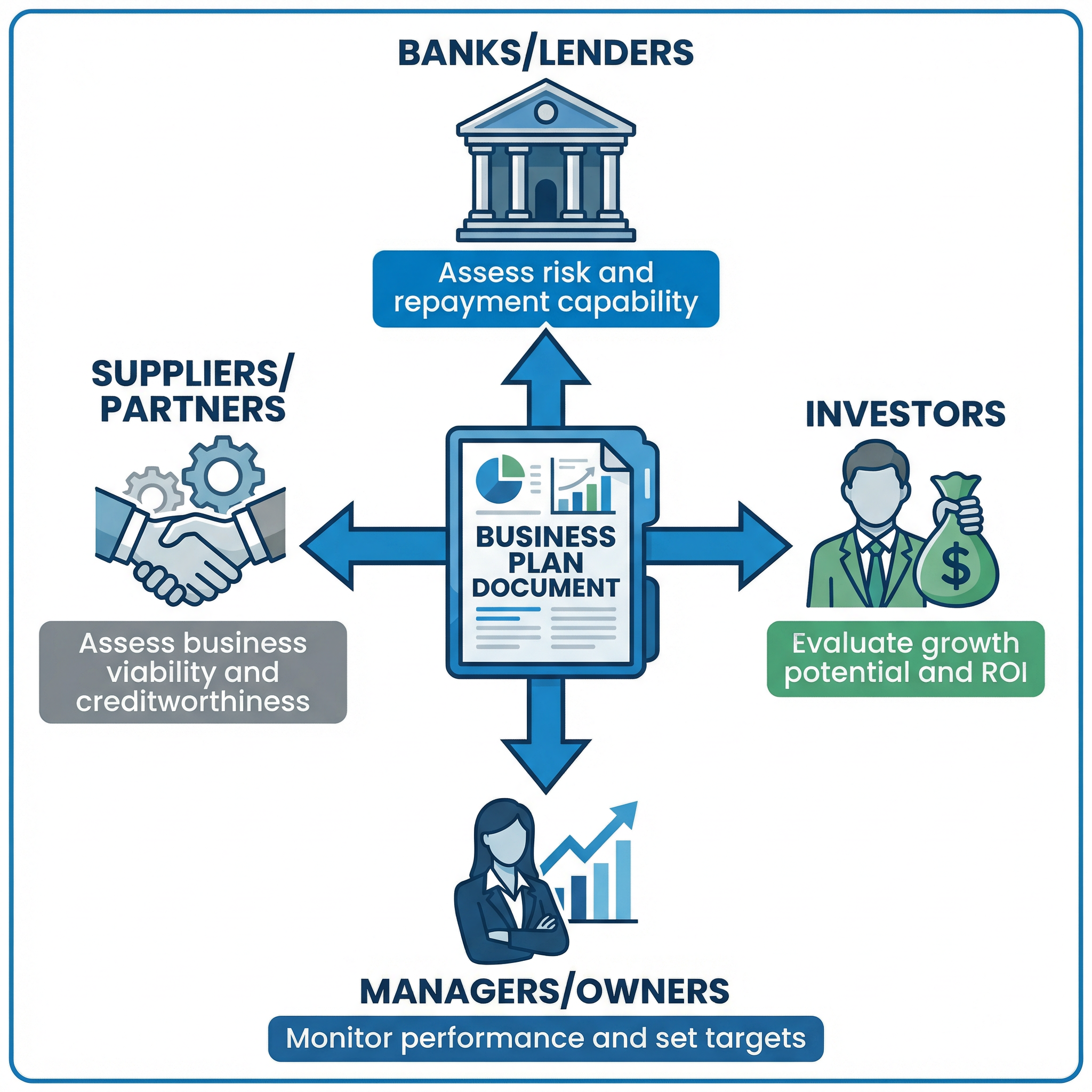
- For Entrepreneurs/Managers: It acts as a roadmap, forcing them to think critically about every aspect of the business. It helps to identify potential problems early and provides a benchmark to monitor performance against targets.
- For Banks and Lenders: They use it to assess the risk of lending money. The financial forecasts, in particular, help them to judge the business's ability to repay a loan.
- For Investors: They are interested in the potential for growth and a return on their investment (ROI). The marketing strategy and financial forecasts are crucial for this.
- For Suppliers: They may want to see a business plan to assess the creditworthiness of a new business before offering trade credit.
