Study Notes

Overview
This guide covers the AQA GCSE French topic of Global Issues (Les Problèmes Mondiaux), a core component of Theme 2. Examiners expect candidates to demonstrate a strong command of vocabulary related to environmental problems (l'environnement), social issues (la pauvreté, les sans-abris), and solutions like voluntary work (le bénévolat). Success in this area requires not just knowing words, but using them accurately within complex grammatical structures. Marks are awarded for manipulating different time frames, using the subjunctive mood correctly (e.g., 'il faut que...'), and forming conditional sentences with 'si' clauses to discuss hypothetical solutions. This guide will break down these key areas, providing the specific knowledge and skills needed to impress examiners and achieve high grades across listening, speaking, reading, and writing assessments.
Key Concepts & Vocabulary
This topic is divided into three main pillars. Mastering the specific lexis for each is essential for earning marks.
1. L'Environnement (The Environment)
Candidates must be able to discuss environmental problems and solutions. Pay close attention to gender agreement, as this is a frequent source of error.
Key Vocabulary:
- Le réchauffement climatique: Global warming (masculine)
- La pollution (de l'air/de l'eau): Pollution (of the air/water) (feminine)
- Les déchets (m): Waste / rubbish
- Les gaz à effet de serre (m): Greenhouse gases
- L'énergie renouvelable (f): Renewable energy
- Protéger: To protect
- Recycler: To recycle
- Réduire: To reduce
- Jeter: To throw away
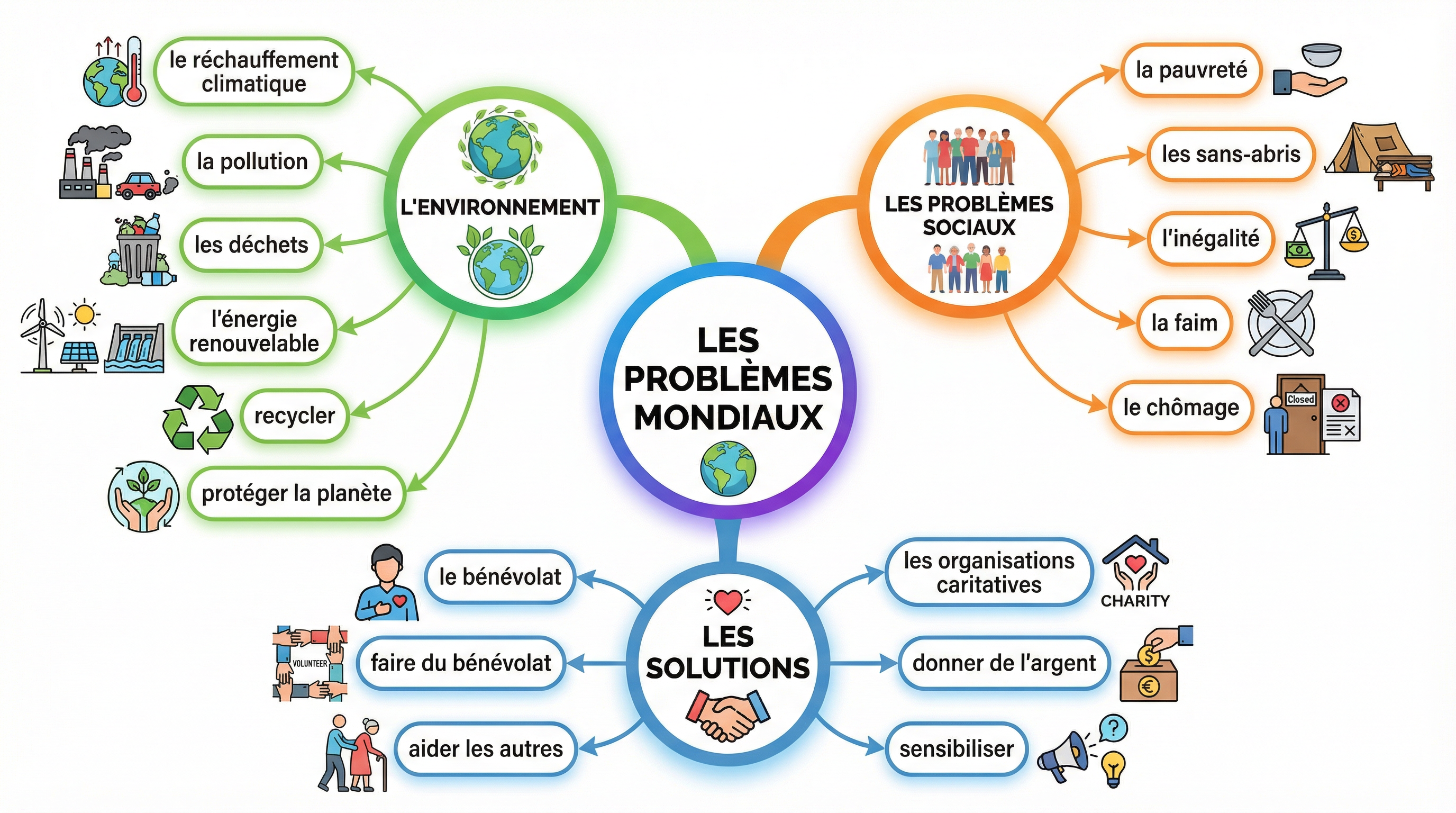
2. Les Problèmes Sociaux (Social Problems)
This section focuses on issues like poverty, homelessness, and inequality. Expressing opinions with justification is key.
Key Vocabulary:
- La pauvreté: Poverty (feminine)
- Les sans-abris (m. pl.): The homeless (Note: always plural)
- Un SDF (un sans domicile fixe): A homeless person
- L'inégalité (f): Inequality
- La faim: Hunger
- Le chômage: Unemployment
- Aider: To help
3. Les Solutions et Le Bénévolat (Solutions and Volunteering)
Examiners look for candidates who can propose and discuss solutions using sophisticated language.
Key Vocabulary:
- Le bénévolat: Volunteering / voluntary work
- Faire du bénévolat: To do voluntary work
- Un bénévole / une bénévole: A volunteer
- Une association caritative: A charity
- Donner de l'argent: To give money
- Sensibiliser le public: To raise public awareness
Grammar for Top Marks
To move into the top bands, you must use complex grammatical structures. Focus on these three.
1. The Subjunctive Mood
Used to express necessity, doubt, or emotion. The key trigger phrase for this topic is 'Il faut que...' (It is necessary that...).
- Structure: Il faut que + subject + subjunctive verb.
- Example: Il faut que nous protégions l'environnement. (We must protect the environment.)
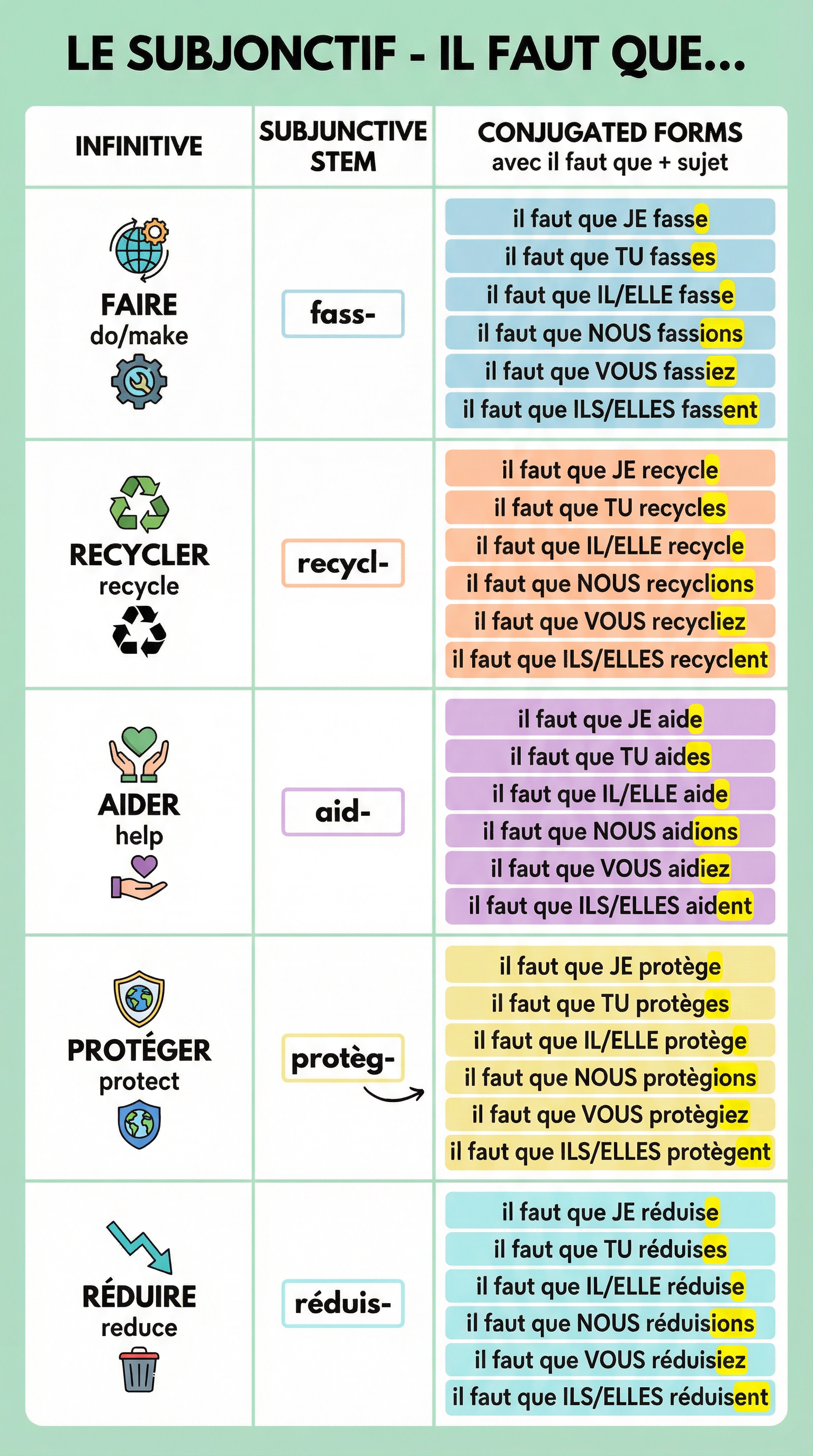
2. 'Si' Clauses (Conditional Sentences)
Used to discuss hypothetical situations and their consequences. Perfect for suggesting solutions.
- Structure: Si + imperfect tense, ... conditional tense.
- Example: Si j'avais plus de temps, je ferais du bénévolat. (If I had more time, I would do voluntary work.)
3. Using Three Time Frames
Demonstrate linguistic flexibility by discussing the topic in the past, present, and future/conditional.
- Past: Avant, on recyclait moins. (Before, people recycled less.)
- Present: Aujourd'hui, la pollution est un problème grave. (Today, pollution is a serious problem.)
- Future: À l'avenir, nous devrons utiliser les énergies renouvelables. (In the future, we will have to use renewable energies.)
